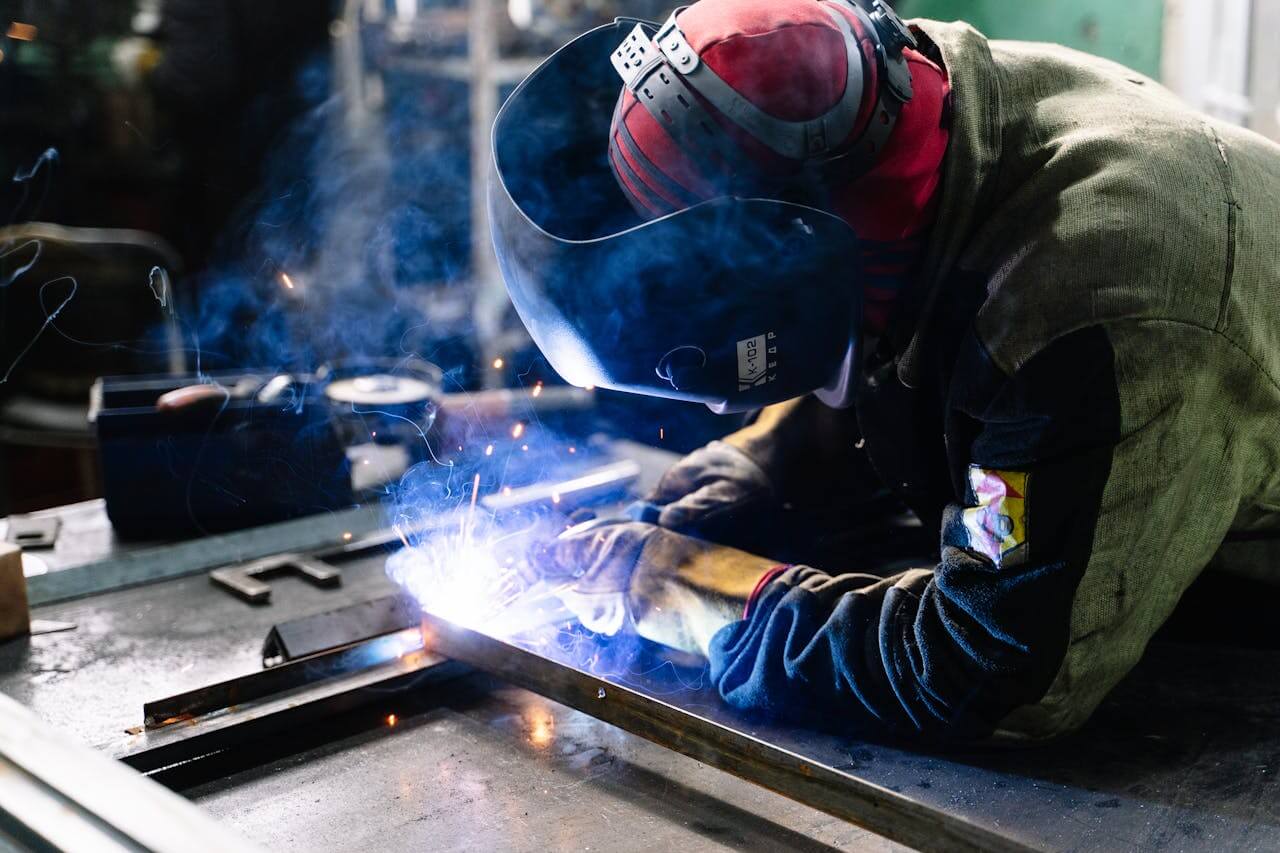
Modern society needs metal-fabricated objects and structures in some capacity in everyday life. Multiple welding techniques exist to suit the kind of metals to be joined together. The metal welding services and welding companies also consider the desired output or structure and the welder’s skill level. These skills and techniques matter because different metals, such as aluminum, steel, and copper, among others, have varying melting points.
ER Machining’s mission is to be the leading company when it comes to all things metal and fabrication in the Houston, Texas area. We have state-of-the-art machinery and are certified to provide certified welding services at our welding shops to meet your metal and fabrication needs promptly, and with professionalism.
The Importance of Welding in Industry
Welding plays a significant role in various industries on which the world depends, for example, aviation, automotive and construction industries, among others. More than 70% of fabricated works come directly from welding. Direct examples where vessel welding plays a role are, in road works, gates, fences, kitchen devices and ware, pipelines, vehicles, planes, space shuttles, and artillery, among others.
While these welding provisions may seem insignificant, the welding industry largely contributes to a country’s economy. The manufacturing industry, in which welding plays a huge role, accounts for 12% of GDP in the USA and employs over 12 million people (data from the American Welding Society).
With increased population growth comes an increased demand for commercial products and infrastructure produced directly or indirectly by the welding industry. It means the industry will contribute even more to the country’s GDP.
Understanding the Welding Process
Welding involves fusing two or more metals, plastic or wood (the original material to be used during welding services is referred to as filler or consumable). It forms a weldment (the resulting joint) from the parent material (the cojoined parts). The different types of welds include the slot weld, plug weld, full penetration weld, and partial penetration weld (partial joint penetration).
Welding methods
1. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
It’s commonly found in construction and automotive settings. Here, a thin wire acts as an electrode to create an electric arc. It heats up as a welder feeds it through a welding instrument while using a shielding gas (carbon dioxide, argon, oxygen or helium) to keep the area free of airborne contaminants and works on stainless steel, copper, and nickel, among others.
2. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW/Stick Welding)
SMAW is a low-cost process that’s not so strong on the quality side. It’s popular among home-shop welders and uses a flux-coated electrode consumable in a manual two-handed process. It has similarities to the TIG method but melts the stick rod and flux coat to emit the gas that shields the welded section from contaminants.
3. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
It’s most common for thin and non-ferrous metals. It’s an advanced welding form centred around patience, experience and skill. Its major difference from other methods is its use of a non-consumable tungsten electrode when forming the weld.
4. Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
FCAW is a distinct two-process welding method where the welder feeds wire continuously during the progression. In one part, shielding gas takes centre stage while in the other, self-shielding agents that are an offshoot of decomposed flux material within the wire enable the process. The latter enables outdoor welding and is typically used in construction due to its high speed and portability.
Others include; Submerged Arc Welding, Thermit Welding, Gas Welding, Forge Welding, Electron Beam Welding, Resistance Welding, Plasma Arc Welding, and Atomic Hydrogen Welding.
The importance of adhering to quality and safety standards in welding.
Adopting safety standards in producing quality welded material ensures the well-being of workers and end product consumers. Having strong welds that will not unexpectedly break, causing injuries is fundamental.
Quality means the aesthetics, which are crucial to consumers, are catered for as well since poorly welded products are easily noticeable. It also all but guarantees the performance, longevity and durability of a product, since the joints will withstand stress and tension easily.
Quality metal works also reflect well on the company that produces the work. Attention to detail, concern for customer wellbeing, regard for quality, taking pride in work done and great customer service are all essential in attracting and retaining customers.
Innovations in Welding Technology:
There is a rise in more efficient welding techniques that increase the speed with which tasks are completed. Robotic welding systems take the lead where the control offered by computers is leveraged to weld metals with enhanced precision and speed. It’s effective and facilitates welder wellbeing. Robotics, the cost-effective approach, will soon lead to the automation of the whole welding industry, eventually eliminating the human error element. It’s possible since the parts follow specific instructions from computer programs.
Laser welding tech is one of the latest advancements in the welding world. The laser beams rapidly melt the metal, fusing the target area as required. The high-precision method enables fine work with the most intricate of parts. It’s estimated to be up to 10 times faster than MIG welding. Since the heat used is moderate, it’s a popular form in medical and automotive work.
Large-format metal additive manufacturing and Robotic metal 3D printing are interchangeable terms that refer to Wire arc additive manufacturing. It is another breakthrough method that fuses automated MIG (metal inert gas) or laser welding with 3D printing. This modern approach has enabled the industrial sector to produce huge metal parts in reduced lead times while eliminating costly supply-chain challenges.
ER Machining and Welding:
At ER Machining, we have a team of certified welders {European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED), National Board Inspection Code (NBIC) and ASME Section VIII} that man the over 400 welding processes. We are committed to customer satisfaction through our modern welding solutions that surpass performance and quality expectations. TIG, MIG, Plasma arc, and Submerged Arc welding processes are our specialty. Our team has several welding credentials from different welding codes.
Environmental Consideration
Welding produces fumes from the metals, fillers, shielding gasses and fluxes, as well as debris and remains that become environmental waste and contaminants. To counter these, ER machining ensures the team cleans usable material of paints, oils and coatings before welding. This minimizes corrosion, rusting and environmental contamination. Where applicable, solvents are used to render these coatings inert and harmless to the environment.
Other than that, we recycle reusable parts, use automation, invest in energy-saving systems, use environmentally friendly energy sources, use fume extraction systems and choose less environmentally impactful processes (like the use of virtual reality in training, which we take seriously, new staff) and consumables. All this is possible while upholding quality standards and putting our clients first.